Check what you know
Did you know?
Key active technologies:
Check what you know
Did you know?
- Advanced Driver Assistance (ADAS) are technologies that assist drivers with the safe operation of a vehicle.
- ADAS safety features are designed to avoid collisions by offering technologies that alert drivers to problems, implementing safeguards and taking control of the vehicle, if necessary.
Active safety describes features designed to help drivers avoid a collision.
Passive safety features come into play following a collision and are designed to reduce injuries to occupants in the vehicle.
Drivers should stay alert and always have full control of their vehicle as ADAS technologies are designed to help drivers to avoid a collision, not take over the task of driving.
Key active technologies:
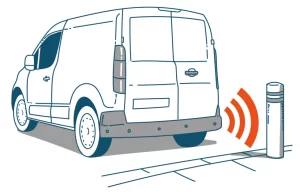 The four more common ADAS technologies are:
The four more common ADAS technologies are:
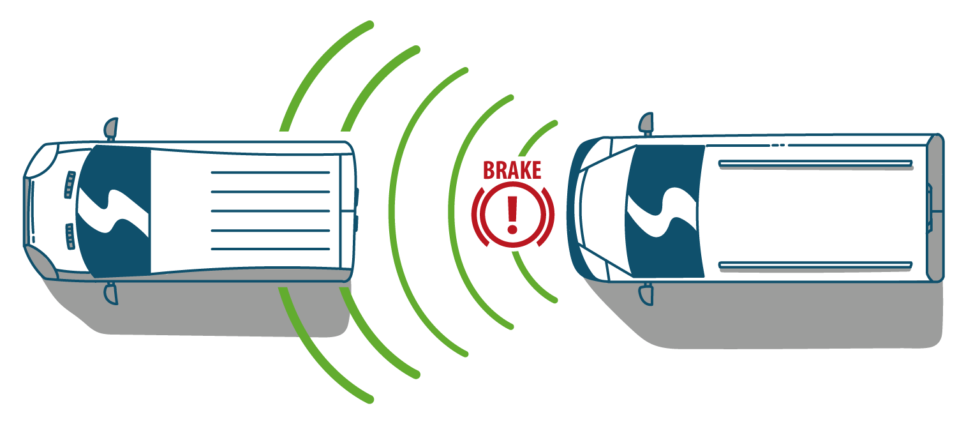
- Advanced Emergency Braking (AEB) AEB will detect and brake for obstructions in front, such as other vehicles, cyclists and pedestrians, if the driver doesn’t react.
- Lane Keep Assist (LKA) Cameras detect the white lines and notify the driver through a tug on the steering wheel if you cross the white line without indicating.
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) ACC maintains a set time-distance to the vehicle in front under a pre-set maximum speed, with the braking and accelerating as necessary.
- Rear Traffic Alert (RTA) RTA identifies approaching traffic when reversing, such as out of a parking space or a driveway.
The Euro NCAP safety rating system helps drivers compare the safety of cars for adult and child occupant protection, vulnerable road user protection and safety assistance systems. The number of stars reflects how well the vehicle performs in Euro NCAP tests, and by the level of safety equipment that comes fitted as standard.

Drivers should always be looking to choose the highest rated vehicle possible. More information can be found at www.euroncap.com
Categories


Crown Copyright 2025
You may re-use this information (not including logos) free of charge in any format or medium, under the terms of the Open Government Licence.
To view this licence, visit www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence